In this article, we will show 2 ways to convert columns into rows in R using the following data:
df <- data.frame(jan_2023 = c(1,1),
feb_2023 = c(2,2),
mar_2023 = c(3,3))
df
# jan_2023 feb_2023 mar_2023
#1 1 2 3
#2 1 2 3
1. Using matrix transpose
The function t() takes the data frame df and returns a matrix where columns and rows are switched:
t(df) # [,1] [,2] #jan_2023 1 1 #feb_2023 2 2 #mar_2023 3 3
But we have 3 problems with this function:
- The output is a matrix instead of a data frame
- The columns (
jan_2023,feb_2023, andmar_2023) are row names instead of values inside a column - The column names (
[,1]and[,2]) are confusing
So let’s clean this output a little bit with the following code:
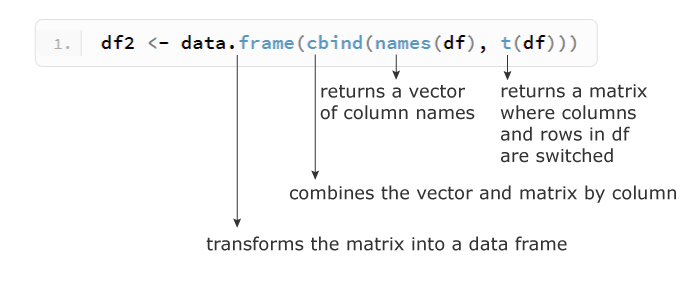
df2 <- data.frame(cbind(names(df), t(df)))
colnames(df2) <- c('date', 'n1', 'n2')
rownames(df2) <- NULL
df2
# date n1 n2
#1 jan_2023 1 1
#2 feb_2023 2 2
#3 mar_2023 3 3
Now the only problem is that the columns n1 and n2 contain character values instead of numbers, which can be easily fixed with:
str(df2) #'data.frame': 3 obs. of 3 variables: # $ date: chr "jan_2023" "feb_2023" "mar_2023" # $ n1 : chr "1" "2" "3" # $ n2 : chr "1" "2" "3" df2$n1 = as.numeric(df2$n1) df2$n2 = as.numeric(df2$n2) str(df2) #'data.frame': 3 obs. of 3 variables: # $ date: chr "jan_2023" "feb_2023" "mar_2023" # $ n1 : num 1 2 3 # $ n2 : num 1 2 3
2. Using pivot_longer
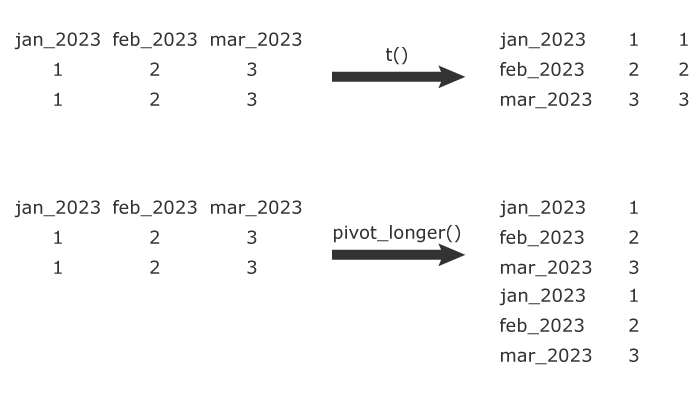
The function pivot_longer() from the tidyr package also transforms column names into rows but in a different way than the transpose function t(). Here’s an illustration that shows the difference between the two:
The general syntax of pivot_longer() is:
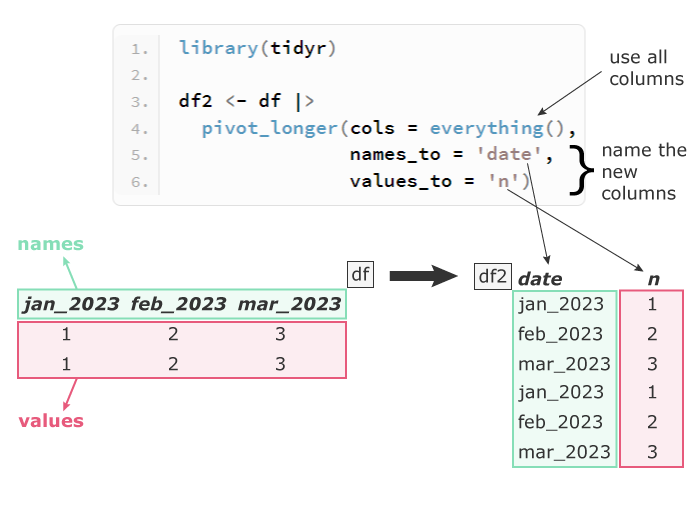
library(tidyr)
df2 <- df |>
pivot_longer(cols = everything(),
names_to = 'date',
values_to = 'n')
df2
## A tibble: 6 x 2
# date n
# <chr> <dbl>
#1 jan_2023 1
#2 feb_2023 2
#3 mar_2023 3
#4 jan_2023 1
#5 feb_2023 2
#6 mar_2023 3
We could have separated the date into 2 columns: month and year; here’s a tutorial on how to do it using pivot_longer().